Neurology Services
This is Photoshop's version of Lorem Ipsum. Proin gravida nibh vel velit auctor aliquet. Aenean sollicitudin, lorem quis bibendum auctor, nisi elit consequat ipsum, nec sagittis sem nibh id elit.
Duis sed odio sit amet nibh vulputate cursus a sit amet mauris. Morbi accumsan ipsum velit. Nam nec tellus a odio tincidunt auctor a ornare odio. Sed non mauris vitae erat consequat auctor eu in elit. Class aptent taciti sociosqu ad litora torquent per conubia nostra, per inceptos himenaeos. Mauris in erat justo. Nullam ac urna eu felis dapibus condimentum sit amet a augue. Sed non neque elit.

Amblyopia or Lazy Eye Services
What is lazy eye or amblyopia?
Medically, lazy eyes is called amblyopic eye. It is the delayed development of visual function in varying degrees in childhood with partial or complete loss of vision. It can affect one or, less often, both eyes. Around 2-3% of the population suffer from this condition. Early diagnosis and treatment by ophthalmologists from the Vision, ocular motility and amblyopia unit for infants before the first 4 years of life is crucial, since that is the period during which the visual cerebral cortex is better suited to visual stimuli, and visual recovery deepens on this, decreasing therapeutic possibilities for up to 10 years
Symptoms of lazy eye or amblyopia
We identify in children some repetitive movements, such as head leaning, constant blinking, eye winking or situations of blurred vision, double vision, approaching objects, redness ......, among others. These signs should alert parents and educators to go to see an ophthalmologist.
Treatment of amblyopia or lazy eye
Depending on its cause, it can be treated with glasses or contact lenses to correct nearsightedness, farsightedness and / or astigmatism, eye vision occlusion to decrease the vision in the dominant eye by patching or eye drops. It is also possible that the ophthalmological specialist might need to recur to ocular surgery.
Prevention
We recommend that, between the time when the child is 3 and 4 years old, an ophthalmological specialist makes the first assessment of visual accuracy and discard any anomalies that may affect the "learning" of the vision and lead to lazy eye. From 5 years of age onwards, it is recommended to perform annual eye examinations with your ophthalmologist.

Astigmatism Services
What is it?
It is a refractive defect (ametropia) which causes the eye to be unable to form a clear image from an object, because the power of the optical system varies between the principal meridians; the higher and lower power.
The main cause is usually lack of corneal symmetry (toricity). Also, there is a degree of toricity in the lens or the retina, among others, which may cause minor astigmatisms.
There are several classifications, according to its regularity (regular and irregular), the direction of the principal meridians (forward, reverse and oblique), or the refractive error (simple or compound; myopic, hyperopic or mixed)
Symptoms
Symptoms include blurred vision present in both near and distant vision. Also, after prolonged visual strain, patients may experience eye pain and occasional headaches. In childhood, uncorrected astigmatism can lead to amblyopia (lazy eye)
By refractive imaging study such as corneal topography (corneal map) the different types of astigmatism are studied in detail.
Treatment
There are several corrective treatments, making it necessary to choose the one that best suits the type and magnitude of astigmatism presented by the patient.
The therapeutic treatment options for correction are glasses and toric contact lenses. For years other option has been laser refractive surgery (PRK and LASIK technique). They are the most used, because of their proven safety and efficiency.
Prevention
Astigmatism is a refractive situation that can not be prevented, but avoid rubbing the eyes may help further stabilization. It is also important to check any suspicions and in children, in order to avoid situations of irreversible visual impairment.
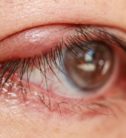
Blepharitis Services
What is it?
Blepharitis is an inflammation or infection of the edge of the eyelids, which causes redness and swelling of the eyelids. It affects the lid margin and specifically the eyelash follicles and the glands located between them. Blepharitis, in general terms, is a benign condition but can cause very unpleasant symptoms. It involves a variety of inflammatory processes, which determines the severity of blepharitis and varies considerably from one individual to another.
Symptoms
Symptoms are often nonspecific and worsen in the morning. They include burning and itching, gritty feeling in the eyes, increased sensitivity to light (photophobia), tearing, eyelid heaviness, excessive blinking and eye pain. The edges of the eyelid look swollen, red and irritated, with presence of scales or yellowish scabs that stick to the base of the eyelashes. Sometimes it occurs with styes or recurrent chalazion. In severe cases this causes the abnormal growth or even loss of eyelashes.
Treatment
The treatment is based on the daily cleaning of the edge of the eyelids. The lid hygiene helps remove bacteria and excess oils. For this, the periodic use of neutral shampoo (not irritating) or special cleansers gently rubbing the edge of the eyelids helps relieve symptoms. Topical (drops or ointments) or oral antibiotics are prescribed in the most severe cases of blepharitis.
Prevention
There is no specific cause of blepharitis, the most common cause is associated with an overgrowth of bacteria in the eyelids. Blepharitis may be associated with predisposing skin conditions such as seborrheic dermatitis, atopic or rosacea. The best prevention is based on exhaustive eyelid hygiene. Regular cleaning of the edge of the eyelids helps remove bacteria and decreases the chance of developing this condition.

Blepharoplasty Services
What is it?
The main function of the eyelids is protecting the eye from external agents (excessive light, foreign bodies, etc.) and distributing tears on the eyeball. But we should not forget that they also play a key role in facial expressions and aesthetics. Over time, the tissues around the eye age, the skin becomes loose and tends to fall, giving our look a sad and tired appearance.
Blepharoplasty is the surgery which corrects the excess skin and bags on both the upper and the lower eyelids. With this surgery we achieve rejuvenating ones look.
Symptoms
Youth is characterized by a clean, smooth, direct and vivid look. This clarity of the gaze is lost over the passage of time, by the overgrowth of skin on the upper eyelids, or the appearance of thick "bags" on the lower eyelids, or wrinkles such as crow's feet, which obscure and sadden the look’s expression. In some cases, excess skin is so abundant that it can compromise a person’s vision. This natural process can be accelerated by hereditary factors, stress, sleep disorders, skin diseases, or excessive sun exposure.
Treatment
It is an outpatient surgical procedure that is performed under local anesthesia and sedation. The upper blepharoplasty is performed through a small incision along the crease of the eyelid, in order to avoid scarring. In the lower lid, if a large amount of excess skin is present, an external incision is also performed following the natural lines just below the lashes; but instead, if the patient reports "bags" but without excess skin, an internal incision is made through the conjunctiva without a surgical scar.
During the first few days after surgery, there may be some degree of inflammation. If we proceed during the first week of surgery with a few sessions of lymphatic drainage, we help eliminate the accumulation of fluid, thereby shortening the postoperative and favoring a speedy recovery.
Within two weeks the patient can resume normal life, and within three months a definite final result can me perceived.
Prevention
Currently we achieve excellent cosmetic results with blepharoplasty, cosmetic eyelid surgery, and the application of botulinum toxin to enhance expression and periocular wrinkles. However, the results could be optimized previously improving skin texture, aged by the passing of time.
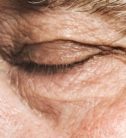
Blepharospasm Services
What is it?
Blepharospasm or "essential blepharospasm" is the involuntary closing of the eyelids. These are involuntary contractions or spasms of the orbicularis muscle (the muscle responsible for closing the eyelids). The course of the disease is gradual. It is one of the most common facial dystonia and occurs for various reasons. Usually it affects people over 50 years old and is more prevalent among women. In addition, there is some genetic predisposition.
When reference is made to blepharospasm, it is appropriate to distinguish between several terms that can be confusing:
Orbicularis myokymia, in which patients perceive eyelid tremors, which are not usually visible to others, and it is frequently associated with stress, caffeine or alcohol. Subsides spontaneously.
Tics, which are voluntary movements of a group of facial muscles. In these cases, although the movements are voluntary, patients are often unable to control them.
Meige Syndrome, which combines spasms of the muscles around the eyes, from the bottom of the face, mouth, tongue, throat and neck.
Symptoms of blepharospasm
The main symptoms of blepharospasm are uncontrollable blinking, involuntary closing of the eyes and even loss of vision in severe cases due to the inability to open the eyelids. At the beginning the symptoms fluctuate, but the pathology progresses gradually both in frequency and intensity. Patients may have difficulty driving, reading, watching television or doing everyday activities of daily living.
Treatment
The treatment of essential blepharospasm is complex, but patients improve with botulinum toxin injections, which temporarily relaxes the orbicularis muscle preventing its contraction. The effect of the injections is temporary and typically lasts a few months, so it is necessary to repeat the treatment to maintain the effect.
For patients resistant to botulinum toxin there is a surgical approach or orbicularis myectomy (removal of the orbicularis muscle, which is the muscle in charge of closing the eyelids). After surgery, it is sometimes necessary to keep the infiltrations of botulinum toxin.
Prevention
The goal of treatment is to help patients to preserve a satisfying lifestyle and minimize the possible disease’s limitations. It is important to protect the eyes with sunglasses and eye drops.
It is essential that all patients with symptoms suggestive of this disease are seen by an ophthalmologists.
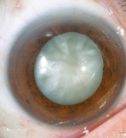
Cataracts Services
What is it?
This condition occurs in the lens, the natural lens inside the eye that allows focusing near and far objects. The lens becomes opaque and loses its transparency, both naturally and due to aging. The images become cloudy and, as it progresses, we lose visual acuity.
Symptoms
The glare of sunlight, lamps or headlights of cars at night is one of most discomforts due to cataracts. Besides blurred distance vision, with many complaints because "the faces of the people cannot be recognized anymore”, these are the most common symptoms. In some cases, cataracts can improve the closer view but at the expense of farsightedness.
Treatment
The cataract surgery is now a quick and painless, highly effective, low-risk procedure. The operation involves removing the clouded lens contents using ultrasound and replacing it with a customized artificial intraocular lens in each case. It allows to regain a normal and even better vision than the patient has had in a long time.
Intraocular lenses are in constant technological evolution, both in design and materials. Currently there are several types of intraocular lenses:
-The Monofocal intraocular lenses, which correct distance vision, but with the patient still needing glasses to see up close.
-The Multifocal intraocular lenses, which can remove the dependence on glasses for near and far vision. More recently, trifocal intraocular lenses have appeared, which provide vision at various distances: near, middle and far.
The indication of one or another kind of intraocular lens must be agreed between the patient and the ophthalmologist, depending on the expectations of each person and their anatomical-functional condition.
The assisted cataract surgery with femtosecond laser is now a painless, safe and quick reality which is given in three phases of the intervention:
-The creation of entry routes through the cornea to the use of instruments.
-The circular opening of the lens capsule, or capsulorhexis.
-The division of the contents of the cataract through small fragments that facilitate the use of ultrasound.
Although the use of ultrasound for cataract extraction is not removed, it does decrease the required applied energy, resulting in a faster recovery for the patient’s eye. The accuracy and safety of these laser assisted maneuvers is greater than can be achieved by the hands of the best surgeons.
Prevention
For incipient cataracts it is possible to take remedial measures, such as wearing sunglasses to avoid glare, or gradual glasses if there has been a change in refraction. But the definitive treatment for cataracts remains surgical treatment. Despite considerable research effort in this area, there is no pharmacological treatment to prevent or cure effectively age-related cataracts.
Dr. Taqi Khalaf is highly specialized and well known for performing thousands of Cataract Surgeries.
Diabetic Retinopathy Services
What is it?
The blood vessels of the retina deteriorate. These altered vessels may be enlarged, causing the escape of fluid (plasma lipids and / or blood), and can even be occluded, leaving part of the retina without blood circulation. All these phenomena which occur due to diabetes can cause progressive damage in very fine structures of the eyeball, leading to a severe decrease of vision and even, without proper treatment, lead to blindness.
Symptoms
The slow progressive decrease of vision in a diabetic person is often translated as the presence of fluid in the central part of the retina ("macular edema"). Sometimes, the disease presents with an acute intraocular hemorrhage, being the first symptom the sudden and very alarming appearance of stains, partially or totally obscuring vision. However, it is important to remember that diabetic retinopathy may be present, even in very advanced stages, and not give rise to any visual discomfort.
Treatment
Some patients with diabetic retinopathy only require periodic monitoring of their eye condition. In other cases, it is necessary to apply laser, selectively, on the abnormal vessels of the retina to reduce edema or on ischemic areas (with no blood flow) to prevent disease progression to more severe forms. In more advanced cases, such as intraocular hemorrhage and / or retinal detachment, we must use methods of intraocular microsurgery (vitrectomy), usually conducted under local anesthesia.
The laser surgery procedures are highly effective in the treatment of diabetic retinopathy, provided they are properly indicated and performed by an ophthalmologist specialized in this disease. Also, intraocular drugs can be used, which may be effective in some cases.
Prevention
Diabetes mellitus is a global metabolic disorder that causes various vascular complications in the body. In addition, when the disease coexists with other general disorders (hypertension, obesity, increased cholesterol, etc.), the risk of ocular complications is multiplied. Therefore, the first recommendation for a patients with diabetic retinopathy is to be very disciplined with taking care of their general health, diet, weight control and the guidelines that will be marked by their endocrinologist. Diabetes cannot be cured, but its good control already implies a great achievement.
https://pennachioeye.com/specialty-eye-care/diabetic-retinopathy/
Dry Eye Services
What is it?
The "dry eye" is a general term applied to all those circumstances where there is a poor lubrication of the eye, affecting the eyelids, the tear layer, the conjunctiva and cornea, a set called ocular surface. The term covers both situations of low amount of tear, poor quality, or excess evaporation.
It is one of the most common reasons for visits to an ophthalmologist due to the inconvenience caused. Factors that influence their occurrence are age, menopause, smoking, refractive surgery such as LASIK or anti-anxiety medications, antidepressants, contraceptives or anthistamines, among others.
Symptoms
The symptoms are varied, and include burning, burning, redness, itching, grittiness and discomfort when performing tasks that require visual fixation, such as reading, driving or using any screen (computer, mobile, TV, etc.) . In addition, these symptoms usually worsen in environments with smoke, dust, air conditioning, wind or low humidity. Also poor tolerance to contact lenses can be an important symptom of "dry eye".
To reach a correct diagnosis and establish the cause or root causes must, the patient undergo a thorough examination by a specialist. A thorough review of the eyelids and its free edge must be performed, determining the frequency of blinking, study the quantity and quality of tear production, measure corneal sensitivity, and sometimes even a biopsy of the ocular surface for a diagnosis. It may be advisable to perform a blood test to rule out autoimmune cause, such as Sjogren's Syndrome.
Treatment
The treatment is long-term and sometimes for life, as the evolution of the disease is chronic, slowly progressive. You always have to consider what the main causes are to keep the balance and tear achieve lasting symptomatic relief.
Basically, the lid hygiene, use artificial tears, avoid irritating environments, the use of goggles and the rest of the view to make visual efforts, helping patients improve symptoms. Adding a diet rich in essential fatty acids, like nuts or blue fish, can also be beneficial. Sometimes the specialist may prescribe antibiotic eye drops, anti-inflammatory or, in severe cases, making serum from the patient's own blood. When an autoimmune case, the patient to a rheumatologist for better systemic medication must be administered morally.
Prevention
Avoiding environments with low humidity or drugs predisposing "dry eye" is often not possible, but the most important thing is to consult a specialist for this disease to reach an accurate diagnosis and put the appropriate therapeutic measures.
https://www.beraja.com/medical-services/dry-eyes/
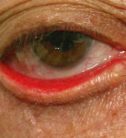
Ectropion Services
What is it?
Eyelids have a fundamental mission in protecting the eye. Eyelids are essential elements and any change in their position can lead to a bad eye protection, alteration of the ocular surface and visual impairment. One of the main eyelid malpositions is ectropion.
In palpebral ectropion the eyelid everts (turns outward). It mainly affects the lower eyelid and causes the eyelid not to touch the eye.
Ectropion is classified according to its aetiology in congenital, cicatricial, paralytic, mechanical and senile, the latter being the most frequent.
Symptoms
In ectropion the eyelid margin loses its normal alignment with the eye. The lid turns outward (away from the eyeball) so that ocular exposure increases and causes chronic irritation with lid margin redness, pain and tearing.
Treatment
The treatment of ectropion is mainly surgical, depending on the severity. They are usually procedures with good prognosis, and are usually performed under local anaesthesia, except in the case of children, which are operated under general anaesthesia.
Prevention
Surgery is usually very effective in restoring the appearance and function of these malpositioned eyelids. It is important that all patients are assessed by an ophthalmologist in this pathology.
Entropion Services
What is it?
Eyelids have a fundamental mission in protecting the eye. The eyelids are essential elements and any change in their position can lead to a bad eye protection, altering the ocular surface and causing visual impairment. One of the eyelids main malposition is entropion.
An entropion occurs where an eyelid turns inwards towards the eyeball. Usually affects the lower eyelid, but may also occur on the upper eyelid.
Entropion is classified according to its aetiology in congenital, cicatricial, spastic, involutional or senile.
Symptoms
In entropion the eyelid margin loses its normal alignment with the eye. The lid is rotated inward (toward the eyeball) so that the eyelashes continuously contact with the cornea, causing chronic eye irritation, pain and tearing. In addition, the constant rubbing of the eyelashes with the cornea can create serious problems as erosions or ulcers, and an itching very uncomfortable to the patient.
Treatment
Treatment of eyelid malposition, including entropion, is surgical, depending on the severity. They are usually interventions with good prognosis, and are usually performed under local anaesthesia, except in the case of children, which are operated under general anaesthesia.
Prevention
Surgery is usually very effective in restoring the appearance and operation of these malpositioned eyelids. It is important that all patients are assessed by an ophthalmologist in this pathology when palpebral alterations occur.
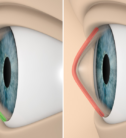
Farsightedness Services
What is it?
An eye that is able to correctly focus images on the retina is called emmetropic eye. If the optics of the eye differs from the emmetropic eye, we talk about defects or errors of refraction.
In hyperopia, the eye is smaller than the emmetropic eye length, and therefore the images of distant objects are focused behind the retina. This causes blurring, the greater the closer the object.
Symptoms
People suffering from hyperopia close se worse from near that far. It is the opposite of myopia default. The more diopters of refractive error in a hyperopic eye, the more blurry the seen images will appear when not wearing glasses.
Treatment
Farsightedness traditionally has been corrected with glasses and contact lenses. For years, another treatment option is laser refractive surgery. The most widely used because of its proven safety and efficacy is the technique known as LASIK. It consists in modifying the shape of the cornea to change the eye’s the eye’s refraction, or overall graduation. The epithelium (thin surface layer) of the cornea is carefully separated with an extremely precise femtosecond laser and then applying the excimer laser, modeling the cornea to correct the desired diopter. Finally, the treated area is covered with epithelium, previously separated, without stitches, to restore the normal ocular surface. Within few hours the results are obvious, which definitely improves the following day. Vision stability is generally regained within the first few weeks.
Implantation of phakic intraocular lenses (without removing the lens) could be assessed, in selected cases. This innovative outpatient surgery is very safe and is performed under local anesthesia.
Prevention
Farsightedness is a refractive situation that cannot be prevented, although treatment is effective. It is crucial to have an annual check for farsighted patients and people older than 50 years, due to normal physiological changes that occur in eyes with age.

Floaters Services
What is it?
“Floaters" are characterized as the vision of mobile floating bodies in the form of points, shadows, wire, flies, fabrics or other, traveling through the visual field. It is one of the most frequent reasons for consultation during visits to the ophthalmologist. Although the cause and effect hasn’t been verified precisely, age and myopia have been identified as the main predisposing factors. Structurally, floating bodies correspond to condensations (aggregated collagen fibers) formed on the transparent gel-like fluid that fills the eyeball, called the vitreous humor, and cast shadows on the retina with the passage of light. In most cases, these condensations are a consequence of the natural dehydration that the vitreous suffers.
Symptoms
It manifests itself as a set of spots, dots, or moving filaments (often in the form of web) suspended in the visual field. Characteristically, they move with eye movements and seem to flee when we try to look at them directly. They don’t usually follow exactly the movement of the eyes, and generally they have a slow movement when staring, as if they were "drifting". Floaters are very common, and most people learn to ignore their presence. Typically perceived with greater intensity when vision is fixed on a homogeneously illuminated surface, with a bright background (computer screen, reading or looking at the sky on a clear day). The vitreous detachment also leads to the perception of floaters, usually of acute onset. Myodesopsias of retinal appearance, or associated to the vision of flashes (photopsia), can constitute a very suspicious sign of a breakage in the retina.
The vision of floating bodies is also more common in people operated of cataract surgery, and those which have been subjected to a cleaning of the posterior capsule laser (capsulotomy). Less frequently, floaters can be part of the symptoms of a serious eye disease, whether of inflammatory origin (posterior uveitis), bleeding (vitreous hemorrhage from various sources) or tumor (intraocular tumors).
Treatment
There is currently no effective medical treatment to permanently remove floaters.
In more extreme cases, where the mobile opacities significantly interfere with vision or become a psychologically intolerable problem, vitrectomy surgery might be indicated, whereby the vitreous gel is removed by condensation and replaced with a transparent physiological saline. Vitrectomy is a highly specialized and very effective intraocular surgery, performed under local anesthesia, and does not require stitches Nevertheless, the potential risks, although minimal, are only indicated in cases where symptoms are disabling for the patient.
Prevention
In most cases, floaters are considered a normal and safe circumstances, that does not compromise vision. Often, the patient initially feels very distressed by this symptom; it appears and disappears depending on the backlight, and is usually exacerbates due to fatigue and the state of stress and anxiety of the person affected. However, over time, the majority of people can adjust perfectly to the view of these small moving shadows. When floaters are very dense and have little mobility, they can cause a very symptomatic blurred vision, significantly compromising the quality of life of patients. It is recommended to consult an ophthalmologist to assess all possible causes of the appearance of floaters.
Cornea transplant Services
What is a cornea transplant?
The cornea is a thin transparent membrane that covers the front portion of the eye, in front of the iris and pupil. It plays numerous roles: as a transparent window of the eye it lets the images pass and acts as a powerful lens to focus them on the retina. The retina is a nervous tissue that carries images to the brain and that allows us to see the objects that surround us.
Corneal transplant is a surgery procedure to replace part of the pathological cornea with corneal tissue from a donor.
Signs and symptoms
The cornea can present a number of conditions: opacities (acquired or from birth), edema, or deformation (the most frequent, keratoconus). There are occasions in which the transplant is the only alternative due to urgent pathologies such as trauma, infections or risk of perforation. In the same way it is possible that it is performed for diagnostic reasons.
Treatment
Corneal transplant surgery involves replacing the pathological cornea with corneal tissue from a donor cornea. The tissue meets the legal requirements as well as the analytical tests necessary for the donation according to current legislation.
There are different techniques:
Corneal transplant or penetrating keratoplasty involves cutting the pathological cornea and replacing it with a graft carved from the donor cornea. This is fixed in all its perimeter by fine sutures and left in position for months or even years, until the union of the graft with the recipient cornea is consolidated. There is the special situation of autotransplantation, where the cornea is from the patient is rotated to avoid an opacity, or the cornea of the other eye is used.
Lamellar transplant techniques. Surgical techniques have evolved in recent years, and today it is possible to selectively transplant the affected corneal layers depending on the pathology of every patient There are several lamellar transplant techniques depending on the layers that are replaced (DALK, SALK, DMEK DSAEK)
The introduction of the femtosecond laser to perform the corneal section has also led to an outstanding increase in the precision, reproducibility and safety of this technique.
Results
The main complication in corneal transplants is rejection that depends on the immune response of each patient in front of the graft, although this risk has diminished with the new surgical techniques.
https://advancedvisionsurgery.com/blog/832017swap-over-corneal-transplant
Chalazion Services
What is it?
A chalazion is a chronic sterile inflammatory injury (like a cyst) caused by an oily secretion retained primarily by the Meibomian glands found inside the eyelids. When a chalazion is secondarily infected it is known as internal sty. It can occur at any age and on a recurring basis, and is more common in patients with meibomian pathology or rosacea.
What are the symptoms?
It is usually a painless lesion, but can cause pain if it is inflamed. In very occasional cases a large upper eyelid can press on the cornea causing astigmatism and blurred vision.
Treatment
Treatment may be unnecessary because at least one third of the cases resolve spontaneously, and an internal sty may also disappear.
When there are alterations of the glands, with multiple lesions or recurrence of the same, more specific treatments are required with drops or ointments (lubricants and sometimes anti-inflammatory and antibiotic), eyelid massage with heat and food supplements with omega-3.
Persistent encysted injuries that cause discomfort or aesthetically are not accepted by the patient require surgery for removal or a small injection of corticosteroids in the same lesion especially if it is near the lacrimal punctum.

Dacryocystorhinostomy Services
What is it?
One of the ocular symptoms that bother and concern the population is excess watering of the eye. Although in many situations exposure to cold or wind is normal and very common for eyes to cry involuntarily, some people have this feeling continuously; the epiphora, hindering daily activity and making it a condition that requires evaluation by an ophthalmological specialist.
Dacryocystorhinostomy (DCR), is an innovative laser-assisted technique for the treatment of lacrimal obstruction, minimizing complications presented when using classical technique.
Symptoms
Under normal conditions, our tears must drain the eye towards the nostrils, in order to meet a circuit that protects our eyes and allow us the constant turnover of moisturizer. But sometimes the "drain" of the lacrimal system can be altered in its size and even become clogged. This situation results in a constant, disturbing and pathological tearing that can affect everyday life, in addition to producing frequent and recurrent infections (dacryocystitis) that constitute a contraindication to cataract surgery. The lacrimal duct must be repaired before the intervention, in order to eliminate the risk of infection involved.
Treatment
The most common type of lacrimal obstruction is the one that affects the end of the tear trail, in the bottom of the tear duct, where it meets the nose bone. Correction of this condition has a very effective solution; the dacryocystorhinostomy (DCR). This surgical technique is based on making a new bone in the lacrimal bone window to connect the lacrimal sac to the nose in order to overcome the obstruction that has been created.
Classical or external DCR has two complex issues: access to the skin between the eye and the root of the nose, which in a small percentage of people may leave a scar and the possibility of bleeding. Despite this, in experienced hands surgical success reached about ninety percent.
The DCR assisted laser diode is performed with laparoscopic techniques, using a camera and a digital screen. Based on the same principles as the classical technique, access is via the tear duct without skin incisions. It is also much less aggressive with the tissues, so that the possibility of bleeding is negligible. It is a developing technique, already used as a forerunner in our center since 1984, and it continues to evolve. It is a way of intervening via the tear duct with minimal aggression to the organism, allowing incorporation into active working life early.
Prevention
It is essential to have an excellent selection of patients because only part of the people with tear obstruction will be susceptible to laser intervention. Variables such as the area of obstruction, age, sex, and history of prior infection or surgery will be key to assessing the adequacy of treatment. It is therefore appropriate that, in situations in which tearing becomes an annoyance, the patient must see an ophthalmologist, who will assess in each case the possibilities to solve this change in the most effective way.

Glaucoma Services
What is it?
Glaucoma is defined as an irreversible optic nerve disease which may be due to several causes, and whose most important risk factor is elevated intraocular pressure (IOP). The importance of this disease is evident, as is the second cause of blindness in developed countries.
We speak of glaucoma when we find that the optic nerve is affected (this acts as a conductor of information from the eye to the brain). Furthermore, ocular hypertension occurs only when IOP is elevated. IOP is determined by the production rate of the aqueous humor (ocular fluid responsible for the tune), and the resistance and difficulty in its drainage.
There are many types of glaucoma, although in general terms it can be classified according to their origin (primary or secondary) and according to the angular amplitude (open or closed angle).
Symptoms
Since the majority of patients suffering from glaucoma often have no symptoms until entering advanced stages of the disease, and considering the irreversibility of the damage, it is vitally important to diagnose the disease in its earliest stage.
The predisposing factors are: age over 40, family history, nearsightedness, diabetes, hypertension and cardiovascular diseases, among others.
Treatment
Most treatments are designed to increase drainage and possibly reduce the production of aqueous humor. The cornerstones of treatment are three, from least to most invasive:
Medical-Pharmacological: using eye drops, to be applied once a day, two or three depending on each. In very specific cases they may be given tablets.
Laser: very safe and on an outpatient basis. There are three modes. Laser iridotomy, usually preventive. Very effective in acute glaucoma attack. Laser trabeculoplasty for open angle glaucoma treated by developmental stage and patient age. And finally, the transscleral diode cylclophotocoagulation, focused on treating ciliary processes, producers of aqueous humor.
Surgical: The two most common techniques are non-penetrating trabeculectomy and sclerotomy. As a third option there are valve implants. These techniques enhance the filtration of aqueous humor.
Prevention
It is a chronic disease that requires ongoing reviews and good treatment. Compliance is essential for effective disease control. As an asymptomatic disease in its early stages, early diagnosis is the best ally to control the evolution.
Primary Glaucoma may have a genetic basis, which may or may not manifest. Therefore a very thorough control are advised to children of parents with glaucoma. Moreover, in patients with predisposing factors are recommended to have annual eye tests.

Keratitis Services
Keratitis associated with contact lens use
What is it?
Misuse or poor hygiene of contact lenses can cause various eye problems, including inflammation of the cornea, or keratitis, which can be caused by dryness, tenderness or infection and can lead to vision loss. Contact lenses are elements that we use to neutralize the ametropia (myopia, astigmatism, farsightedness and presbyopia) with very good results and minimal complications. The cornea is the transparent layer above the eye and on her the lens is placed.
We have soft and gas permeable rigid lenses. They can be of daily use, both disposable and reusable, or prolonged use with large oxygen permeability, and they can be slept with for a maximum of thirty days.
Symptoms
Symptoms of keratitis include red eye, foreign body sensation, blurred vision, discharge, tearing, discomfort to light and pain. In cases of severe infection hypopyon (pus deposit in the anterior chamber of the eye) and deep ulceration with risk of perforation
Treatment
It depends on the etiologic agent. If they are caused by herpes virus, even though it usually has little relation to the use of contact lenses, it will be treated with antivirals. Bacterial keratitis, which is the more dangerous Pseudomonas, it is reinforced with topical antibiotics. Those produced by fungi are more resistant and difficult to treat, and can also cause uveitis. They are treated systemically with antifungals. It is sometimes necessary to aspirate hypopyon and washing the anterior chamber in the operating room with diluted antifungal. Another type of keratitis is caused by Acanthamoeba, which has trophozoites and cysts. It occurs mainly in patients with soft lenses bathing in pools or in the sea with them on. They are treated with Antiamoebic for at least 6 months.
Sometimes, in severe cases, it is necessary to complete the clinical treatment with a corneal transplant.
Prevention
For any type of keratitis and treatment we must know what is the cause that produces it, for which we make a detailed history.
Factors contributing to infection with contact lenses are the lack of cleanliness during use, inadequate disinfection, environmental pollution, lack of lubrication, sleep with contact lenses, bathing in pools or in the sea with them or use them more time advised. Contact lenses that produce less infectious problems are rigid, gas permeable or soft disposable lenses. In addition, regular checks for wearers of contact lenses are recommended.
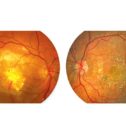
Keratoconus Services
What is it?
Keratoconus is one of the most common degenerative diseases of the cornea. It is the slowly progressive thinning and deformation of the corneal tissue.
It is usually detected in young people starting from puberty, and tends to progress for decades, usually stabilizing after 30 years of age. It may be associated to a large number of local or systemic conditions. It is believed to have a genetic basis, although the importance of environmental factors, such as eye rubbing, should be noted: most patients with keratoconus eyes are chronically and persistently rubbing their eyes.
Symptoms
Myopia and keratoconus typically cause irregular astigmatism, visual distortion with blurring, in young patients who regularly rub their eyes. It can make us suspect and must be addressed by a cornea ophthalmologist specialist.
Treatment
Glasses cannot properly correct it, and semirigid contact lenses must be used. They compensate the irregularity, and although tolerance often become problematic over time, it can be recovered by modifying the curvature of the lens or even combining a soft base on which to mount the rigid lens (piggyback).
Keratoconus has been until recently the leading cause of corneal transplant in our environment, but new techniques are in many cases avoiding keratoplasty:
-Crosslinking (CXL) or collagen raticulation. It is a very simple, safe and effective procedure to stop the progression of keratoconus.
-The implantation of "rings" or intracorneal ring segments (IRS). These are rigid clear plastic pieces (PMMA), arched, which are introduced into the corneal thickness. IRS reduce irregularity and topographic de-centering caused by the cone, while flattening the central cornea.
Prevention
Annual periodic review and environmental measures, as not rubbing eyes continuously, are recommended. When having slightest doubt, consult an ophthalmologist.
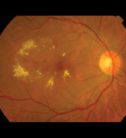
Macular Degeneration Services
What is it?
AMD, or macular degeneration, is the most common cause of severe vision decrease in the western world, and affects people over 50 years of age. The disease causes lesions in the central portion of the retina called the macula. It is responsible for central vision needed for reading, driving or watching TV.
Macular degeneration can be:
-Dry or atrophic: It constitutes 85% of all cases. It presents a slow evolution over time (years).
-Humid Or exudative: is characterized by new formation of blood vessels that grow under the macula. These vessels are called neovascular membranes. Their evolution is quick (days / weeks) and severely compromises central vision.
Symptoms
No pain is presented, but it can present a series of visual symptoms that the patient must recognize: straight lines may appear wavy or broken, estimating distances and heights can be altered, sensitivity to light can be increased, as well as the need for an increased amount of light for reading. There may be blurred vision in the central part of the vision; also, when the disease is in an advanced stage, there can be a black spot in central vision, making it darker and larger the greater time of evolution has.
The diagnosis comprises:
• Examination of visual acuity
• Ophthalmological examination, paying special attention to the condition of the macula
• Fluorescein angiography. It involves the intravenous injection of a contrast for further study of their behavior at a choroid and retinal (fundus) level.
• Optical coherence tomography. It is a scanner of the macula, which is designed to detect the presence or absence of a neovascular membrane.
Treatment
Major advances in the field of macular degeneration mainly focus on the wet or exudative form. Until a few years ago there were only laser treatments. More recently, intravitreal injections with anti-angiogenic factors appeared as new treatments. Their action blocks the progression of neovascularization. The introduction of some drugs has allowed to achieve better visual results. The average amount of intravitreal injections per year is between 5 and 6. This is an outpatient basis treatment requiring no income. Currently, 70% of treated patients a year manage to not lose sight, and 40% get away with visions above 0.5, which implies the possibility of driving.
Prevention
The visual prognosis of untreated wet AMD is bad. Hence, early diagnosis is key to start treatment as early as possible. In patients who have already suffered a wet AMD in one eye can have a 50% chance of having a neovascular membrane in the other eye, depending on predisposing lesions that exist in the contralateral eye. Therefore it is important to periodically check these patients.
Macular Edema Services
What is it?
The central area of the retina, called the macula, is the area that concentrates the most concentrated amount of sensitive cells (cones), and for this reason it is considered one of the most noble parts of the eyeball. The integrity of the macula allows for clear central vision, distinguishing details, reading and recognizing the faces of people, for example.
Macular edema is a common condition, and is caused by an abnormal accumulation of fluid resulting in the expansion and thickening of the intra and extracellular space of the macula, due to a change in the permeability of the capillaries which irrigate it.
It may happen during the evolution of various vascular eye diseases (diabetic retinopathy, the most common, venous thrombosis, perifoveal telangiectasia, radiation retinopathy), during inflammatory processes (anterior or posterior uveitis, vasculitis), postoperative eye surgery (cystoid macular edema or Irvine-Gass syndrome after cataract surgery, even if completed without any complications), in certain congenital dystrophies of the retina (retinitis pigmentosa), associated with intraocular tumors, tensile phenomena (epiretinal membrane syndrome vitreomacular traction), in macular degeneration and even in relation to the use of certain topical eye drops for glaucoma treatment (prostaglandin analogues).
Symptoms
Typical symptoms are blurred and usually painless slowly progressive central vision, although occasionally the disease appears quickly (eg in venous thrombosis of the retina) and the perception of distorted images may appear.
The most common clinical method for determining the presence or absence of macular edema is the stereoscopic clinical examination or with the slit lamp biomicroscope. However, sometimes it is necessary to use additional imaging, optical coherence tomography which allows to evaluate changes in the morphology and thickness of the macula. Fluorescein angiography is a useful test to evaluate the circulatory condition of the retina, where an intravenous contrast material is injected.
Treatment
Effective treatment of macular edema must be based on recognition of the pathogenic factors that cause it. The options are many and include various medical treatments (eye drops, intraocular and periocular injections), laser photocoagulation and vitreoretinal surgery, identifying the best option for each case.
Prevention
These cases usually have a good prognosis with a simple medical treatment, even though a good control of predisposing factors, such as diabetes mellitus or hypertension, among others, is fundamental.
The prognosis is very variable in each situation, and it is convenient in all cases to consult an ophthalmologist retina specialist for accurate diagnosis and the most appropriate treatment.

Myopia Services
What is it?
Myopia is an alteration in refraction, in which distant objects are focused in front of the retina instead of on it. This causes the vision of such objects to appear blurred
Symptoms
Symptoms vary for myopia, but the blurring caused when trying to focus on distant objects is most prominent. This causes the image of such objects to appear blurred. Its onset occurs in childhood and often progresses throughout adulthood
Treatment
Treatment should be individualized in each case, but the treatment options are the correction with glasses and contact lenses. For years, the other option has been laser refractive surgery (PRK and LASIK technique). These are the most used, because of their proven safety and efficacy. In addition, in selected cases there are other surgical technique such as implantation of phakic intraocular lenses (without removing the lens) or aspirating the lens and implanting an intraocular lens (same technique would realize at an early cataract of high myopia).
Prevention
Every patient with myopia should conduct an annual eye examination in a strict regime, since this disease has a significant functional impact.

Presbyopia and Accommodation Services
What is it?
It’s possible that the vision problem which ends up affecting a greater number of people is presbyopia, more commonly known as "eyestrain". It is currently estimated that there are 1,800 million people affected by presbyopia, and by 2020 there are expected to be 2,300 million. It is not therefore surprising that the possibility of solving presbyopia through surgery has become one of the new frontiers in ophthalmology.
Presbyopia is the result of the loss of accommodation, the physiological capacity that allows us to keep a sharp image of an object as this approaches us. Accommodation involves an increase of the optical power of the eye, by bringing the focal point from a far point to a closer one, like when reading. To focus 33 centimeters (cm) from the eye, starting from the further focus, we must accommodate 3 diopters (D).
Symptoms
Accommodation decreases with age, and by the age of 40 only about 3 or 4 D remain: the patient begins to notice difficulties when read comfortably without the aid of glasses. After 40 years of age, presbyopia makes itself increasingly evident until the accommodation reaches its minimum at 65 years.
Some people in the age of presbyopia can apparently read unaided. Although this may be due to many factors, it happens most often when presenting a slight defect such as myopia or myopic astigmatism. They require less amplitude of accommodation to see closely; however, at the age of presbyopia, even myopic people need a different correction to see clearly from near and far.
Treatment
Currently, in addition to reading glasses, bifocals and progressive lenses, there are multifocal and bifocal contact lenses. Another effective option is called monovision, which consists in correcting one eye (dominant) for far vision and the other one for near.
None of surgical methods proposed so far have been able to restore the correct adaptation, meaning the dynamic and continuously variable ability to focus at all distances; there is only a certain form of remedy at a greater or lesser extent, which is called pseudo-accommodation.
The most used treatments include include bifocal, multifocal and variable focal intraocular lenses (IOL). In general, this surgery is similar to cataract surgery, exchanging the lens with an IOL. The optics for near and far in the same IOL are superimposed, and simultaneously produce near and far focal points on the retina. From this disposition, some limitations in visual quality and defects in night vision are derived, but it is the brain that ultimately chooses the image you are interested in at all times, and adaptability can compensate for many of the system imperfections.
Corneal techniques for presbyopia include monovision, by conventional laser procedures (LASIK or similar type) correcting one eye for each distance, as well as the creation of bi- or multifocal corneas (PresbyLASIK). The main disadvantage is the practical irreversibility of corneal ablative laser procedures.
Intracranial implants can be inserted in the thickness of the thin corneal lenticules, by either lifting a flap as LASIK or creating an interlaminar pocket. These implants can be of refractive type (intracorneal lens), even for a bifocal cornea, or in diaphragm shape without optical power. Sufficient sharpness is achieved for a wide range of distances, from near to far.
Prevention
Although various exercises and nutritional supplements (such as lutein) have been proposed to delay the onset of presbyopia, there is no scientific evidence for their effectiveness.
New accommodative IOL designs appear, some of which may meet a patient’s expectations. One way to really recover the physiological accommodation would be the substitution of the content of the lens with a transparent and elastic gel that would fill the capsular bag (Phaco-ersatz). This idea is not new, but for its practical application it must still overcome some technical problems. Finally, with the advent of ultrafast lasers (femtosecond), the possibility of surgery in the lens without affecting its transparency begins to raise, eventually regaining its elasticity and accommodative function.
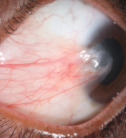
Pterygium and Pinguecula Services
What is it?
Among the most common and oldest-known eye diseases are pterygium and its minor variant, pinguecula. These are growths on the eye surface from the conjunctiva, a totally benign effect of ultraviolet rays (UVB), but may cause irritation and impaired vision.
Symptoms
Many patients come to the doctor complaining of "a lump or lining on the white of the eye" which can be red and irritated, or grow "into the apple of the eye". It is usually a pterygium or pinguecula.
Pinguecula elastosis is a plaque, whitish or yellowish (as in "fat"). Sometimes it bulges and irritates. The pterygium is more aggressive, with growth into the cornea, with a greater tendency to swell. It can affect vision by distorting the cornea, causing astigmatism or directly if it progresses to the central area.
Treatment
If irritative episodes occur, pinguecula may require lubricants and anti-inflammatory eye drops. It will rarely be subject to removal, only if ignited frequently or for aesthetics. In pterygium, however, it is common indication for surgery. However, it remains a troubling problem for its sometimes-reappearing tendency, to recurrence.
In recent decades, much progress has been made for the treatment of pterygium, achieving a significantly reduced recurrence rate. Several strategies can be combined according to their severity. First, a clean surgery, completely removing pathological tissues. Sometimes it can help judicious use of anti-metabolites. But the most decisive was recognizing the importance of reconstructing the ocular surface by transplants (often of the conjunctiva itself). It is a painless outpatient surgery under local anesthesia.
Today, biological adhesives allow do it without stitches. The postoperative is simple, but a few weeks are needed until the appearance of the eye returns to normal.
Prevention
These diseases are more common in tropical countries and especially in mountain areas. Epidemiological studies correlate with the UV dose received throughout life, either by geographic cause, or professional sports; sunglasses or even hats are useful for prevention.
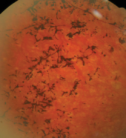
Retinitis Pigmentosa Services
What is it?
It is the most common cause for hereditary retinal degeneration. Numerous genes (12 have been identified) can provoke it, being 50% of cases of hereditary nature (autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive and X-linked), and the remaining 50% appearing in sporadic forms, with no known family history. However, there are environmental factors that can affect protecting or favoring its progression. In recent decades, significant progress in understanding the various factors involved in its appearance and development have been made, although there is still a long way to go.
Its origin causes degeneration and apoptosis (cell death) of the photoreceptors (cells of the retina), canes (responsible for peripheral vision field) and in the final stages of the cones (central vision), causing blindness.
Symptoms
Retinitis pigmentosa (RP) appears quietly and slowly, so usually, affected do people not go to the ophthalmologist until about 15 years after the onset of night blindness symptoms. The age of onset is varied preferably between 25-40 years to develop. Cases occur in children under 20 years and, less frequently, cases in which the disease begins to show its symptoms past 50 years.
The first symptoms that should alarm us are night blindness or, what is the same slow capacity to adapt to the dark, the progressive loss of visual field, which will lead to having tunnel vision. In addition, there may be defects in color vision, and loss of central vision, which does not affect all people equally, even within the same family, finding elderly patients with normal visual acuity for their age.
The prognosis in Retinitis Pigmentosa depends on the form of inheritance and age of presentation. The later the disease appears, the better it is.
Treatment
Neuroprotective therapies, stem cell treatments, or gene therapy represent an important future for the treatment of these diseases, although their current therapeutic options are limited.
An electronic retinal prosthesis that allows an artificial vision has been developed in 2007. Results were valid and it gain approval for use in patients with Retinitis
The system is based on the placement of an intraocular implant that acts as an electrical epiretinal stimulator, placed on the surface of the retina. The system uses a pair of glasses to support an HD camera that is placed over the bridge of the nose. Said camera captures the images that will be processed and, through a pacing system, reach the occipital cortex. Patients recover mostly perception of shapes, objects and movement in their surroundings, allowing them to regain some degree of interaction with himself/herself, as well as independent movement.
Prevention
The characterization of mutations in genes already involved in RP and thus the etiology based on DNA analysis, is, at present, a high cost and laborious task. Another option under consideration is the transplantation of stem cells in the retina.

Retinal Detachment Services
What is it?
Retinal detachment is the separation of the neurosensory retina from the underlying tissue (retinal pigment epithelium), caused by the accumulation of fluid between the two. There are three mechanisms that can cause retinal detachment. The rhegmatogenous type, which is the most common type, is caused by a retinal tear that can occur after a vitreous detachment. The tensile type, which is typical in proliferative diabetic retinopathy and the exudative type, when there are problems or vascular permeability secondary to tumors.
Symptoms?
The most common initial symptom of the rhegmatogenous type, although not always present, is the sight of flashing lights, sometimes repetitive and perceived on a single sector of the visual field. This may indicate the presence of a retinal break, condition that may lead to retinal detachment. However, the light flashes do not always appear as a symptom. The appearance of a shadow, like a curtain which blocks the partial or even full vision in one eye, is a possible symptom of detachment.
In the presence of any of these symptoms, you should go urgently to an ophthalmologist to examine the retina by pupil dilation and through ultrasound, if necessary, to facilitate the diagnosis.
Treatment
The treatment, always surgical, requires the relocation and adaptation of the retina and can be done internally (through vitrectomy) and externally (through indentation). Sometimes a combination of both techniques is necessary. Adhesion is achieved by inducing a thermal lesion with a laser, or generating a scar stimulus through freezing (cryotherapy). Sometimes, depending on the case, the use of intraocular gases or intraocular silicone oil may be necessary.
In some cases, preventive laser treatment for retinal breaks with uncomplicated detachment is advised.
The speed and degree of visual recovery will depend on each individual case. Overall prognosis of retinal detachment depends mainly on its size, if it does not affect or the point of maximum vision (the macula), and on its time of evolution.
Prevention
An annual ophthalmologic examination with pupil dilation is recommended, in order to check the retinal periphery. Laser over degenerative lesions likely to cause a landslide will be applied. In any case, the earliness in the diagnosis and proper treatment are essential for a good outcome of the process.
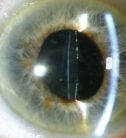
Secondary Cataracts Services
What is it?
Cataract surgery involves removing the cloudy lens using ultrasound, leaving the capsular "sack" that contains it almost completely transparent and introducing an intraocular lens inside. To do so we make a small window in the front of the "sack" (anterior capsule), a clear membrane, leaving intact the posterior capsule lens and the intraocular lens implant within. Said posterior capsule may become cloudy, months or years after cataract surgery, leading to decreased vision. This is called "secondary cataract". This is due to the migration and proliferation of lens epithelial cells from the equatorial and anterior capsule to posterior capsule.
Symptoms
The most prominent symptoms include decreased visual acuity, months or years after cataract surgery, that hinders both distant and near vision, plus the glare of the sun or the lights of the cars at night.
Treatment
To restore lost vision, an opening or window is made in the center of the posterior capsule (capsulotomy), by applying a laser (Nd:YAG). The Nd:YAG capsulotomy is a simple, painless procedure, and on an outpatient basis. It is performed a few minutes after dilating the pupil, under the effect of a few anesthetic drops, and the patient can return home immediately with a treatment in beads. The visual recovery is full (if no other retinal eye disorders, optic nerve or corneal disorders are present) and fast, with noticeable improvement within a few hours. A few days later we conduct a visual inspection to check the evolution and a review to assess the need, if any, to change the glasses. In any case, the capsulotomy improves vision as much as possible.
Despite being a very safe procedure, some patients report seeing "floaters" a few days later, possibly due to small residual fragments of the capsule which are normally reabsorbed and disappear within a few days, although in isolated cases this feeling may persist a longer time.
It is a definitive treatment in a single session, although in very exceptional cases the opacity comes back, making it necessary to repeat the process.
Prevention
It is complicated to prevent or delay opacification of the posterior capsule, although this does not occur in all patients. There are several factors that could delay it, such as a comprehensive polishing of the capsular epithelial cells during cataract surgery, although some authors suggest the opposite. Moreover, certain intraocular lenses, due to their large footprint on the equator of the capsular bag, provide a "bridge" of growth of the epithelial cells into the posterior capsule. The most important thing is to know the symptoms, identify them, and treat it if possible.
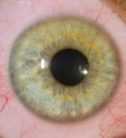
Spring Conjunctivitis Services
What is it?
One of the most common ocular allergic processes is spring conjunctivitis. It can affect people of any age, although the peak of incidence is between 18 and 35 years of age, with no differences between males and females. Usually there is a genetic factor, so people with a family history of allergies are more likely to develop it. The most common allergens in this condition are pollens from trees (olive, banana or cypress) and grasses.
Symptoms
Itching is the main symptom of this disease. In addition, there may be tearing, red eyes, swollen eyelids, discharge and eye pain. In more severe cases it may present discomfort to light (photophobia) and blurred vision. Symptoms usually occur in both eyes, but sometimes in only one.
There is a clear relation between annoyance and the time of year that circulate allergens. It may be associated nasal damage, such as allergic rhinitis, or throat.
Treatment
It is recommended to visit your ophthalmologist as soon as the discomfort begins, in order to assess the status, severity, and provide the most appropriate treatment.
In mild seasonal allergic conjunctivitis, topical antihistamines are used. In moderate or extraocular damage, such as nasal or skin damage, antihistamines are administered orally. In more severe cases it is indicated the association of topical corticosteroids. These can have side effects depending on their potency, duration of treatment and response for each person, which is why the use of these drugs should always be prescribed and monitored by the ophthalmologist. In cases of severe allergy, systemic corticosteroid administration may be necessary.
Prevention
When faced with seasonal allergic conjunctivitis, allergy tests should be performed to determine the causing allergens and assess treatment with vaccines, which is usually effective in the long term.
Environmental control is the most important preventive care for people with this disease. To accomplish this, one should avoid exposure to the offending allergen, although this may be difficult in many cases. Avoiding or reducing field trips, closing the windows, the use of air conditioning filters and the use of sunglasses during periods of pollination are recommended methods. When the exposure has already occurred, washing with saline or artificial tears can be performed to clean allergens from ocular surface, reducing the contact time. Through these preventive measures it is possible to prevent eye allergy symptoms from recurring year after year.
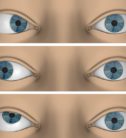
Strabismus Services
What is it?
Strabismus is the condition when the visual axes of both eyes are not directed towards the visual object of interest. Strabismus in infants or children is the most common eye disease, as it affects 4% of children. The development and maturation of the monocular and binocular vision requires a long learning process that begins at birth and continues until eight / nine years of age. The first four are of greater progression, decreasing afterwards.
The muscles of each eye eyeball move towards the object we look, and the images captured by each eye are fused into one with characteristics of relief and depth, what is known as stereopsis, or 3D view.
The muscular coordination mechanism also allows the eyes remain fixed on a stationary object, to follow when moving and maintain fixation on the object when the observer moves. When any of hese circuits and connections fail, strabismus occurs, resulting in sensory and motor impairment.
Symptoms
The sensory alteration is the brain blocking the view of the deflected eye to avoid double vision (diplopia). If this situation persists over time, it leads to loss of vision from the turned eye, causing amblyopia, or lazy eye, as well as the binocular relationship (fusion and stereopsis). When strabismus is alternating, in either eye, ambliopia does not occur, but it does lead to loss of binocular vision. Motor impairment affects the deficit static position and muscle spasms. According to the direction, strabismus types include: horizontal (convergent or divergent), vertical, torsional or mixed. It can affect one eye or be alternating, presenting itself as constant or intermittent. Intermittent, up to six months it can be considered as physiological, given the neurological immaturity of the infant (strabismus in infants).
Treatment
Some kids are squinting due to uncorrected refractive defects (farsightedness, nearsightedness and astigmatism) as in the case of accommodative esotropia, which occurs in farsighted patients. The treatment will first be medical, in order to improve amblyopia by occlusion or penalty with filters adapted to the glass or by droplets in the better eye and refractive error where it exists, with glasses or contact lenses. If strabismus persists, according to magnitude and clinical characteristics will be completed with surgical treatment. Strabismus surgery involves weakening the overactive muscle by modifying its insertion, and strengthening the deficit muscle by shortening it in length, in order to achieve maximum alignment. The muscular injection of botulinum toxin can be an alternative to surgery in certain clinical cases and orthoptic exercises stimulus binocular vision, may be useful as an adjunct to surgery in selected cases.
Prevention
The neonatologist and/or pediatrician is responsible for the exploration of the newborn and its immediate evolution. Educators and teachers can be helpful to detect problems in these early ages. The specialist ophthalmologist should necessarily perform a scan at three years of age, even without the presence of any symptoms, and another one five/six years before the maturation of the visual system.
Thyroid eye disease Services
What is it?
It is an affectation of the orbit associated with an autoimmune thyroid disease. It goes by various names: endocrine exophthalmos, thyroid eye disease, thyroid orbitopathy, Graves ophthalmopathy or thyroid eye disease. Various diseases can affect the thyroid. Those which affect its functioning as a producer of hormones are the most common causes. Hypothyroidism, produces a defect of activity, and hyperthyroidism excess. Thyroid eye disease is an autoimmune disorder. This means that the immune system acts against certain cells in the body, in this case against tissues around the eyes (orbital fat, muscles that move the eyes or eyelids).
Symptoms
The first eye symptoms are mild and include dryness, redness, swelling of the eyelids, and inability to wear contact lenses. Often affects worse at night and under certain conditions, such as air conditioning, heating and on windy days.
Inflammation and edema affect the orbit and cause retraction of the eyelids, increasing openness and displacing the eye outwards, giving the appearance of "look of horror" (exophthalmos).
When the extrinsic muscles of the eye become inflamed, even if there is exophthalmos, they may lose motility resulting in double vision (diplopia) and strabismus. In severe cases these compressions create tension and altered vascularity on the optic nerve endangering vision.
In Graves Basedow disease eye symptoms usually occur while thyroid alteration, although it is variable. It is noted that most patients with Graves' disease do not present orbital involvement and, if that would be the case, it would be mild.
Treatment
Inflammation and edema affect the orbit and cause retraction of the eyelids, increasing openness and displacing the eye outwards, giving the appearance of "look of horror" (exophthalmos).
When the extrinsic muscles of the eye become inflamed, even if there is exophthalmos, they may lose motility resulting in double vision (diplopia) and strabismus. In severe cases these compressions create tension and altered vascularity on the optic nerve endangering vision.
In Graves Basedow disease eye symptoms usually occur while thyroid alteration, although it is variable. It is noted that most patients with Graves' disease do not present orbital involvement and, if that would be the case, it would be mild.
Prevention
Effective treatment of hyperthyroidism is no guarantee that the eye disease will improve, and no thyroid treatment can guarantee that the eyes will not continue to deteriorate. Once started, the disease of the orbit can remain active for several months and even years. Later, have a gradual and complete recovery. After a period of inactivity of six months, recurrence of ophthalmopathy orbit is rare. It is noted that orbital involvement is more common and more severe in smokers.
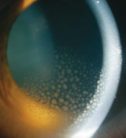
Uveitis Services
What is it?
Uveitis is an inflammation within the eye that affects one or more of the three parts of the uvea: the iris (which gives color to the eye), the ciliary body (behind the iris, where the aqueous humor is produced) and choroid (behind the retina). It accounts for 10-15% of cases of blindness in developed countries and can occur at any age, being more common in young or middle-aged patients. They are classified, according to their anatomical location, as anterior uveitis, intermediate, posterior and panuveitis. Anterior uveitis, which is the most common form, affects the iris (iritis), and sometimes the ciliary body (iridocyclitis). Intermediate uveitis affects the ciliary body and structures near him. In posterior uveitis the choroid (choroiditis) is affected, but often also affects inflammation adjacent to be in direct contact with it (chorioretinitis) retina. Sometimes the three parts of the uvea are compromised, leading to panuveitis.
Symptoms
The symptoms depend on their location. The above and intermediate uveitis cause redness, eye pain, tearing, photophobia (intolerance to light) and blurred vision. Later on, floaters are usually present (perception of floaters), and vision loss, variating depending on the size and location of lesions. Inflammation can occur in only one eye or both (simultaneously or separately in time). It can have acute and sudden, or have a chronic course with a more gradual and longer onset. Relapses or recurrences may be infrequent, and depending on the degree of inflammation they can lead to blindness, bilateral irreversible in some cases. The origin of intraocular inflammation can be very diverse. We divide the causes in idiopathic (without finding the causes infectious and noninfectious (immune or traumatic). Infectious agents include viruses (such as herpes), bacteria (such as tuberculosis or syphilis) or parasites (such as toxoplasmosis, most common infectious cause). The source of infection cannot only affect the eye or be associated with systemic diseases (such as juvenile idiopathic arthritis, etc.) During the initial study and monitoring, most patients may be required blood tests, X-ray examinations or other special additional tests. In specific cases it may be necessary to make a puncture or biopsy inside the eyeball to search cells, inflammatory or DNA molecules, in order to help a more accurate diagnosis.
Treatment
Treatment depends on the cause that results in inflammation, and should be started as soon as possible. In those of infectious origin, antibiotic treatment can be curative. In most patients, corticosteroids are the mainstay of treatment in the acute phase, being in the form of eye drops, injections around or within the eye, or systemic (oral, intramuscular or intravenous). In some immune deriving, chronic, and difficult to manage uveitis or having complications arising from the use of corticosteroids origin, the use of immunomodulatory drugs may be needed to control inflammation (for a long time or even for life). Some of these drugs can have side effects requiring frequent monitoring. In other cases it may be necessary to perform surgery with diagnostic purposes to treat some complications of intraocular inflammation (especially in chronic forms), such as cataract, glaucoma, persistent opacity of the vitreous, intraocular bleeding, or retinal detachment.
Prevention
A thorough eye examination and a complete medical history, both general and ophthalmologic, is essential to be able to investigate the cause of the inflammation. Uveitis is one of the eye diseases that most often can be related to other diseases of the human body (arthritis, Wegener's granulomatosis and other systemic vasculitis), making it convenient to have a multidisciplinary management and study that includes an internist or rheumatologist.
Other Services
Vision Screening
Cross-Linking
Glaucoma Surgery
Cataract Surgery
Kids Vision Screening
Trans PRK + PRK
Oculoplastic Surgeries
Botox injections
DCR
Diabetic Eye screening
Glaucoma screening and management
All minor surgeries e.g Chalazion Incision
Doctors

Dr. Taqi Khalaf

Manal Al Sairafi

Dr. Mohamed Taqi Khalaf

Sayed Husain Khalaf

Sayed Mohamed Khalaf

Ameena Al-Wadaei

Qadreya Almeshqab

Dr. Imad Hamzah

Dr. Mohamed Shaker

Dr. Reema Shabib

Dr. Maryam Almohsen

Dr. Alaa Jaffer

Dr. Hasan Ebrahim

Raichel Varughese

Sobith Kallen

Farveena Saleem

Mia Salve

Abdulla Abduljabbar

Maria Katrina

