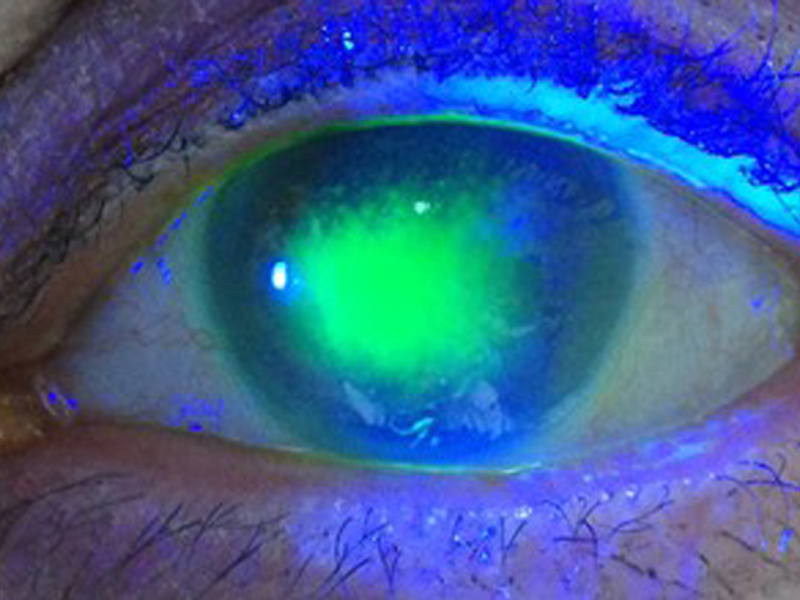
Dry Eye
What is it?
The “dry eye” is a general term applied to all those circumstances where there is a poor lubrication of the eye, affecting the eyelids, the tear layer, the conjunctiva and cornea, a set called ocular surface. The term covers both situations of low amount of tear, poor quality, or excess evaporation.
It is one of the most common reasons for visits to an ophthalmologist due to the inconvenience caused. Factors that influence their occurrence are age, menopause, smoking, refractive surgery such as LASIK or anti-anxiety medications, antidepressants, contraceptives or anthistamines, among others.
Symptoms
The symptoms are varied, and include burning, burning, redness, itching, grittiness and discomfort when performing tasks that require visual fixation, such as reading, driving or using any screen (computer, mobile, TV, etc.) . In addition, these symptoms usually worsen in environments with smoke, dust, air conditioning, wind or low humidity. Also poor tolerance to contact lenses can be an important symptom of “dry eye”.
To reach a correct diagnosis and establish the cause or root causes must, the patient undergo a thorough examination by a specialist. A thorough review of the eyelids and its free edge must be performed, determining the frequency of blinking, study the quantity and quality of tear production, measure corneal sensitivity, and sometimes even a biopsy of the ocular surface for a diagnosis. It may be advisable to perform a blood test to rule out autoimmune cause, such as Sjogren’s Syndrome.
Treatment
The treatment is long-term and sometimes for life, as the evolution of the disease is chronic, slowly progressive. You always have to consider what the main causes are to keep the balance and tear achieve lasting symptomatic relief.
Basically, the lid hygiene, use artificial tears, avoid irritating environments, the use of goggles and the rest of the view to make visual efforts, helping patients improve symptoms. Adding a diet rich in essential fatty acids, like nuts or blue fish, can also be beneficial. Sometimes the specialist may prescribe antibiotic eye drops, anti-inflammatory or, in severe cases, making serum from the patient’s own blood. When an autoimmune case, the patient to a rheumatologist for better systemic medication must be administeredmorally.
Prevention
Avoiding environments with low humidity or drugs predisposing “dry eye” is often not possible, but the most important thing is to consult a specialist for this disease to reach an accurate diagnosis and put the appropriate therapeutic measures.